Abstract
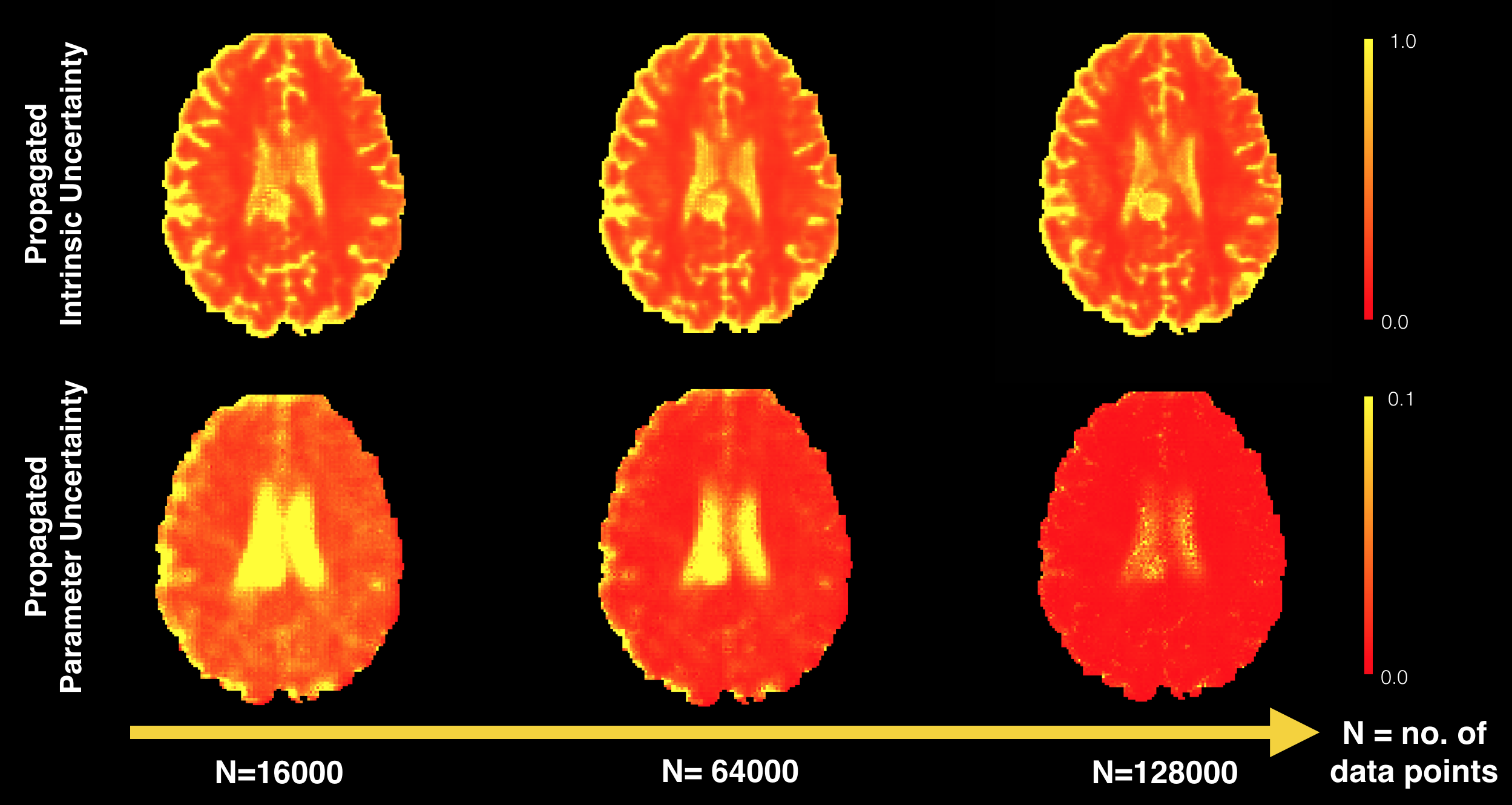
Deep learning (DL) has shown great potential in medical image enhancement problems, such as super-resolution or image synthesis. However, to date little consideration has been given to uncertainty quantification over the output image. Here we introduce methods to characterise different components of uncertainty in such problems and demonstrate the ideas using diffusion MRI super-resolution. Specifically, we propose to account for “intrinsic uncertainty” through a heteroscedastic noise model and for “parameter uncertainty” through approximate Bayesian inference, and integrate the two to quantify “predictive uncertainty” over the output image. Moreover, we introduce a method to propagate the predictive uncertainty on a multi-channelled image to derived scalar parameters, and separately quantify the effects of intrinsic and parameter uncertainty therein. The methods are evaluated for super-resolution of two different signal representations of diffusion MR images—Diffusion Tensor images and Mean Apparent Propagator MRI—and their derived quantities such as mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy, on multiple datasets of both healthy and pathological human brains. Results highlight three key potential benefits of uncertainty modelling for improving the safety of DL-based image enhancement systems. Firstly, incorporating uncertainty modelling improves the predictive performance even when test data departs from training data. Secondly, the predictive uncertainty highly correlates with reconstruction errors, and is therefore capable of detecting predictive “failures”. Results on both healthy subjects and patients with brain glioma or multiple sclerosis demonstrate that such an uncertainty measure enables subject-specific and voxel-wise risk assessment of the super-resolved images that can be accounted for in subsequent analysis. Thirdly, we show that the method for decomposing predictive uncertainty into its independent sources provides high-level “explanations” for the model performance by separately quantifying how much uncertainty arises from the inherent difficulty of the task or the limited training examples. The introduced concepts of uncertainty modelling extend naturally to many other imaging modalities and data enhancement applications.